In the following post, we will talk about what is in the exam. The number of papers. Weightage. Skill assessment. We will assume that you are familiar with the eligibility requirements. So, we won’t go into all that here.
For easy access, we’ve divided the post into several sections. Let’s begin.
What is in the CA Intermediate Exam?
What’s on this page:
The Papers of the CA Intermediate Exam: Overview
The Papers of the CA Intermediate Exam: Skill Assessment
Group I – Paper 2: Corporate and Other Laws
Group I – Paper 3: Cost and Management Accounting
Group II – Paper 5: Advanced Accounting
Group II – Paper 6: Auditing and Assurance
Group II – Paper 7: Enterprise Information Systems & Strategic Management
Group II – Paper 8: Financial Management & Economics for Finance
Passing Requirements and General Tips
Introduction
The exam is officially known as the Chartered Accountants Intermediate exam. CA Intermediate between friends. ICAI is the conducting body. The exam is held twice yearly. Once in May and the other in November.
For the CA Intermediate exam, there are two groups of papers. Group I and Group II. Each group contains four papers. Each paper is held in a single day. You can choose to attempt all papers in either or both groups.
The exam mode is offline. It contains both subjective and objective parts.
The medium of the exam is either in English or Hindi. You’ll have to indicate which when you register. Note that your choice of language is group based. That is, if you registered for a group with the choice of, say English, you must attempt all papers of that group in English. Likewise, for Hindi.
We will talk more about that later and what each paper contains.
But not everyone can register and appear for the exam. You’ll need to fulfil some minimum criteria. To get an idea of the criteria, take a look here. And here are details of the registration process.
The Papers of the CA Intermediate Exam: Overview
As we said there are two groups of papers in the exam. Each group consists of four papers.
Here are the papers of Group I.
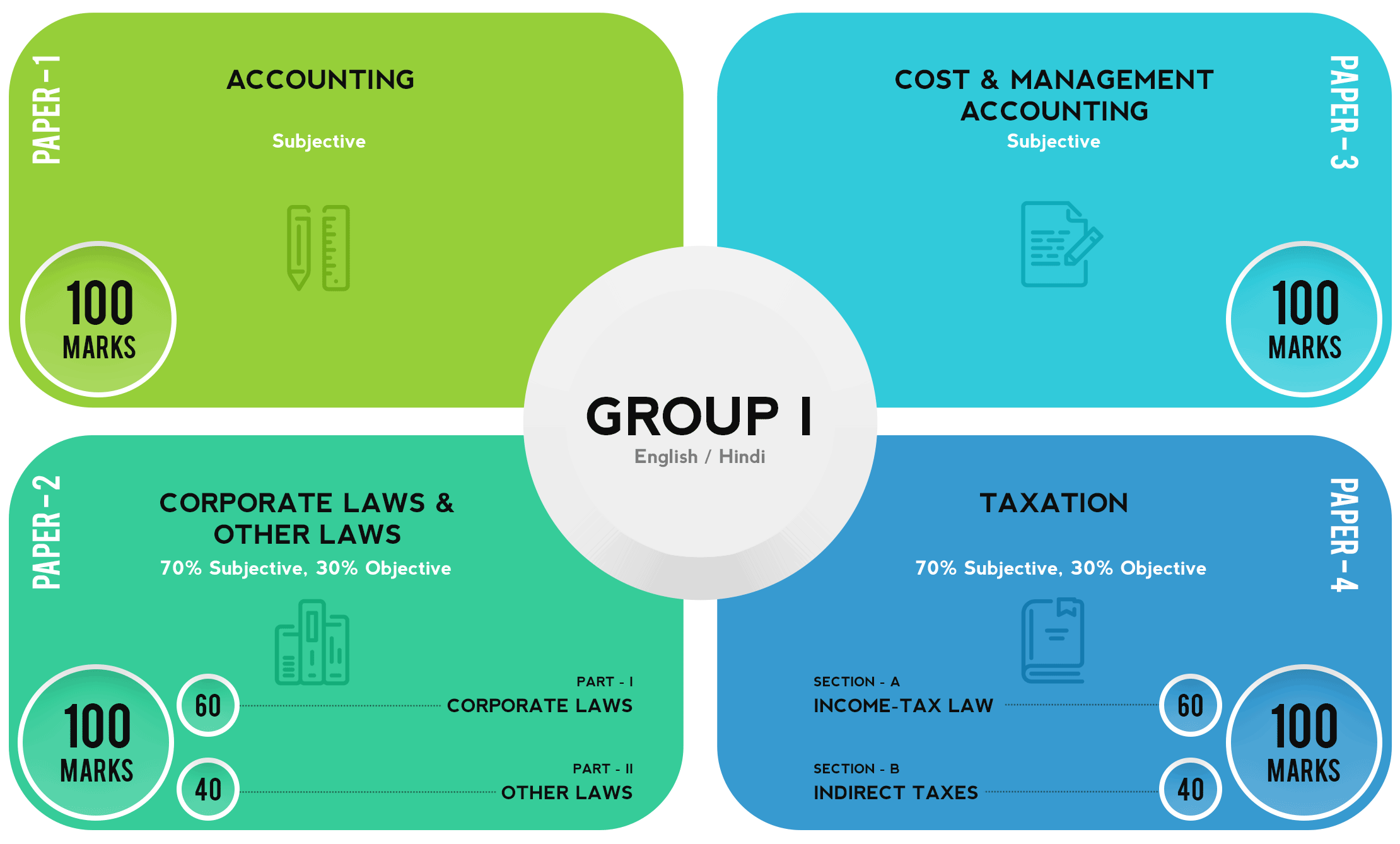
Fig (1): Papers of CA Intermediate Exam Group I
Note that papers 1 and 3 are completely subjective whereas papers 2 and paper 4 are a combination of both subjective and objective parts. 70% weightage is subjective and 30% weightage is objective. The objective part will contain MCQs worth 1 mark each. There will be no negative marking. The objective section is compulsory.
The papers of Group II are as follows:
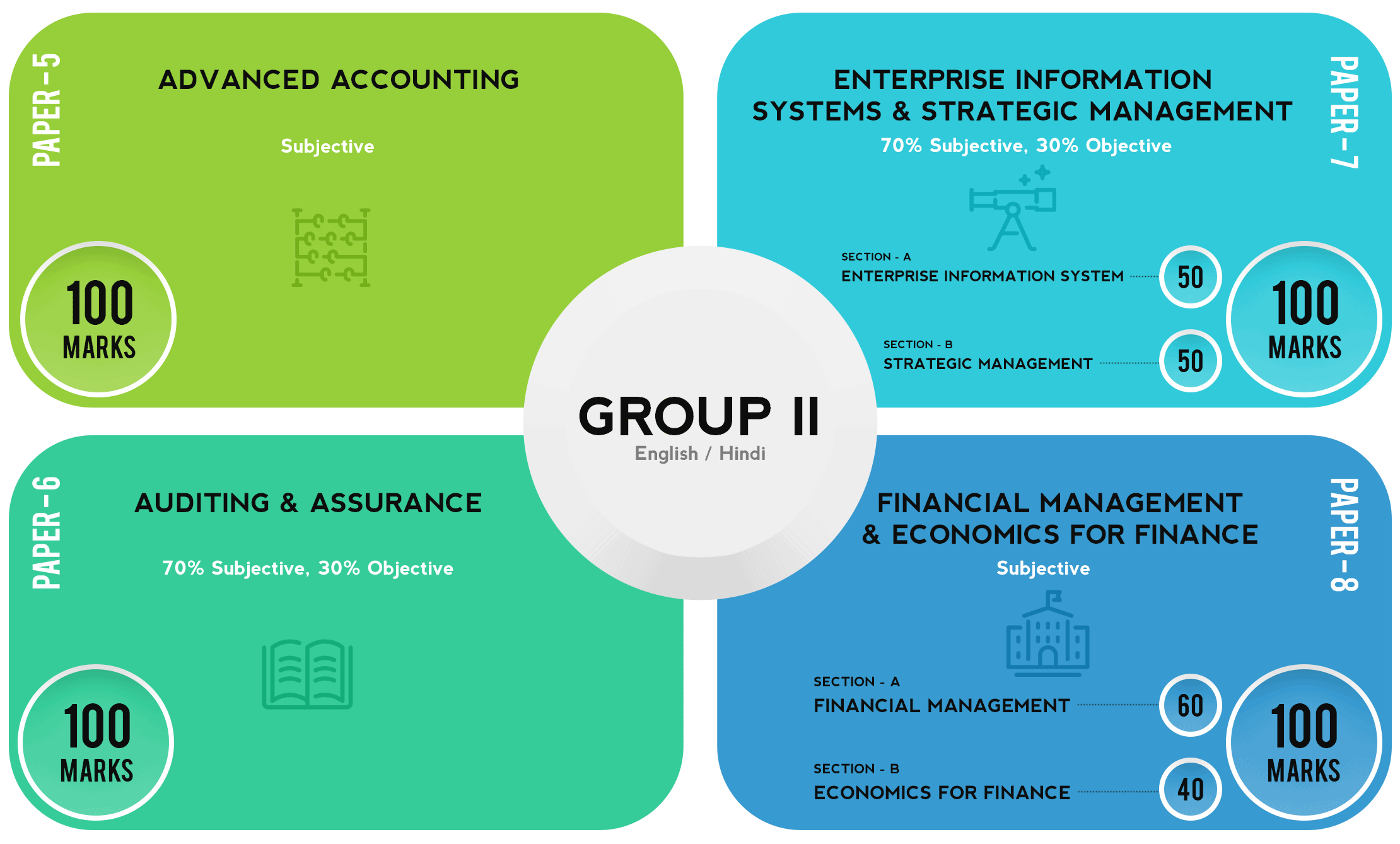 Fig (2): Papers of CA Intermediate Exam Group II
Fig (2): Papers of CA Intermediate Exam Group II
Note that papers 6 and 7 are a combination of both subjective and objective parts. The weightage is 70% subjective and 30% objective. The objective part will contain MCQs worth 1 mark each. There will be no negative marking. The objective section is compulsory.
The Papers of the CA Intermediate Exam: Skill Assessment
ICAI assess different types of skills in each content area. For the whole Chartered Accountancy course, there are three levels of skills: Level I, Level II and Level III. The understanding is that the skills specified in Level I are inherent in Level II. And so on. That is, you cannot achieve Level II skills without having Level I skills first!
Here is the assessment specification grid (taken from the prospectus and adapted for the CA Intermediate Exam.)
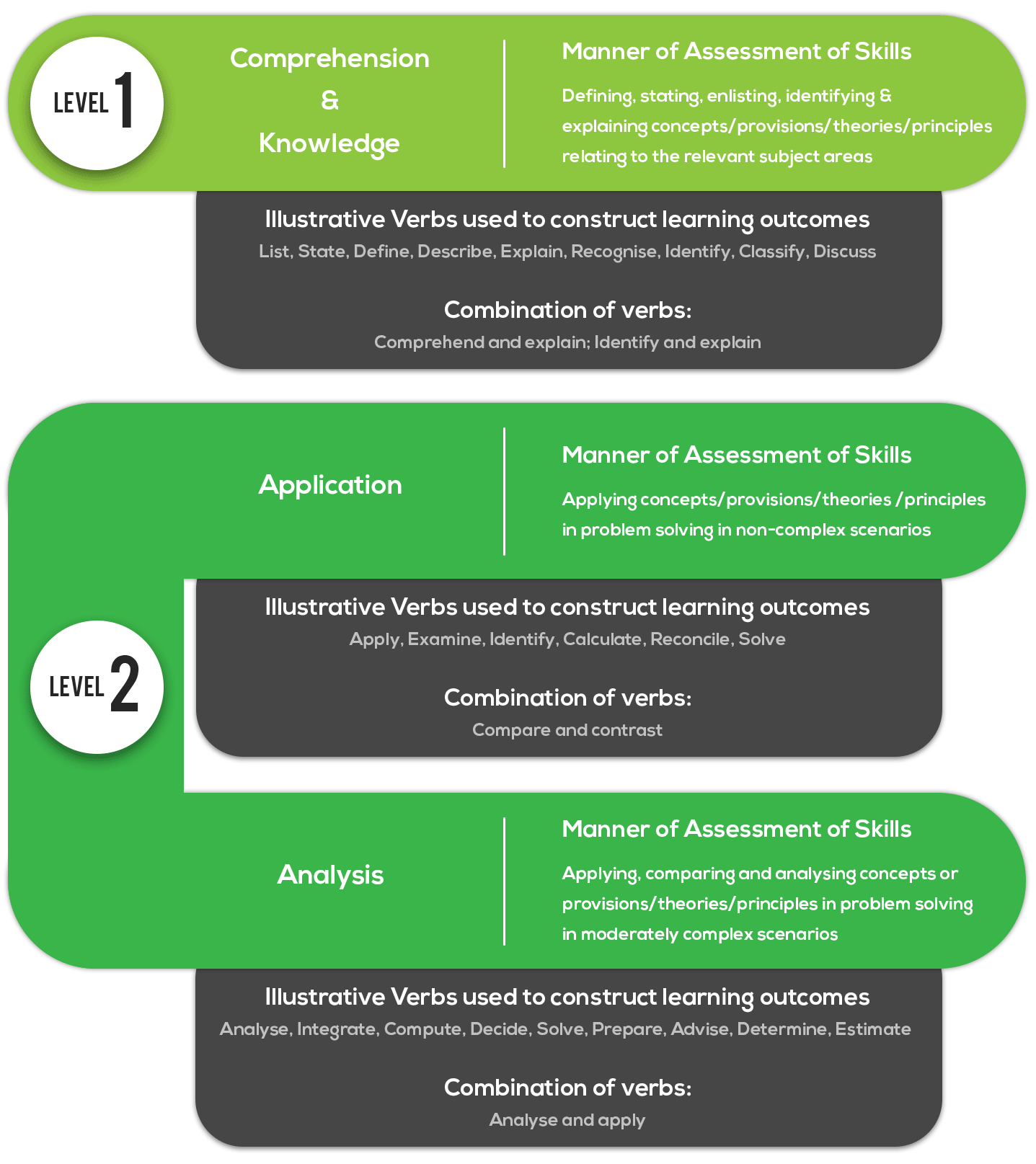
Fig (3): Skill Assessment Grid for CA Intermediate Exam
For skill and level wise weightage for each subject in each paper of Group I, look at the table below:
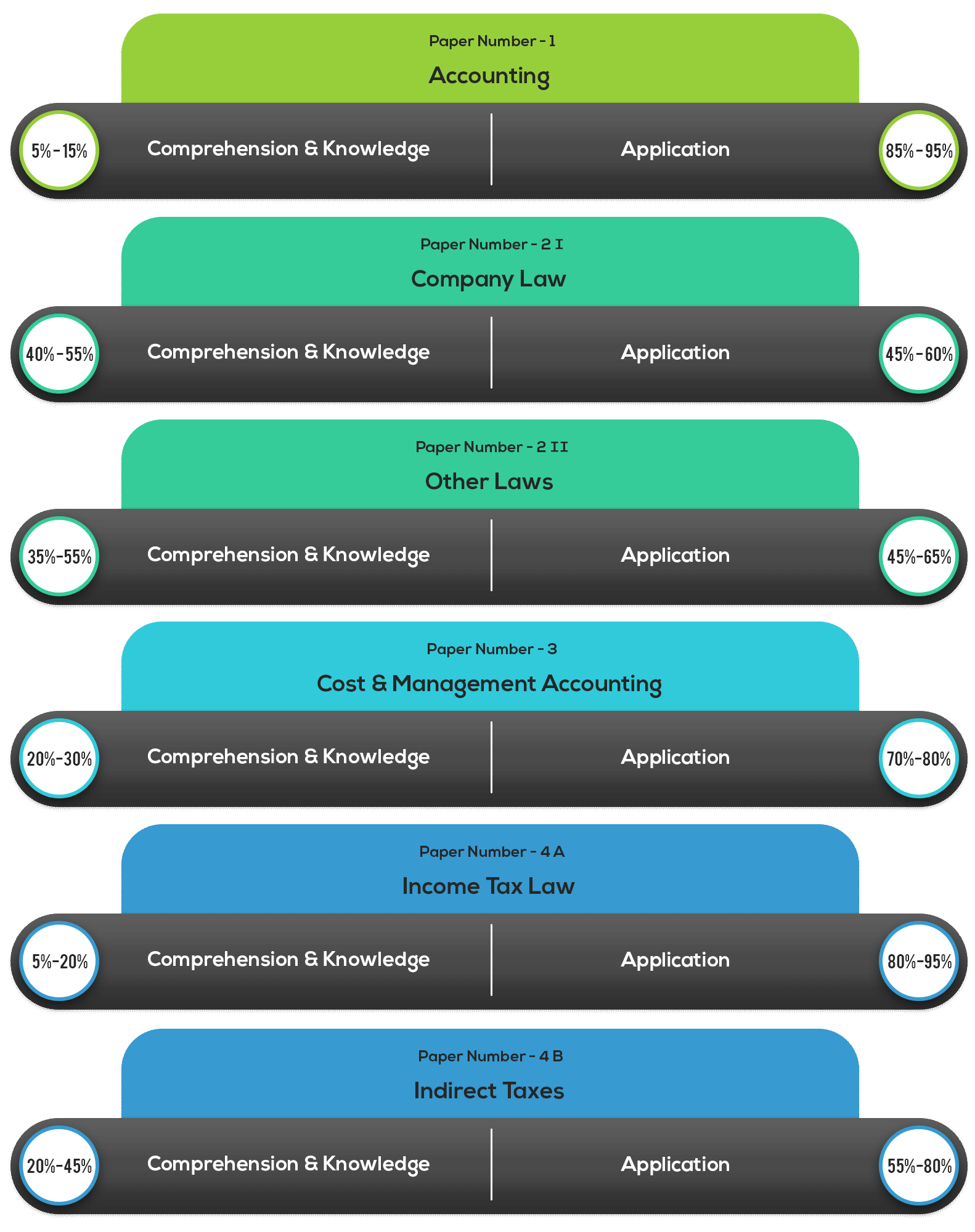
Fig (4): Skill Weightage for CA Intermediate Exam Group I Papers
For papers of Group II, these are the weightage:
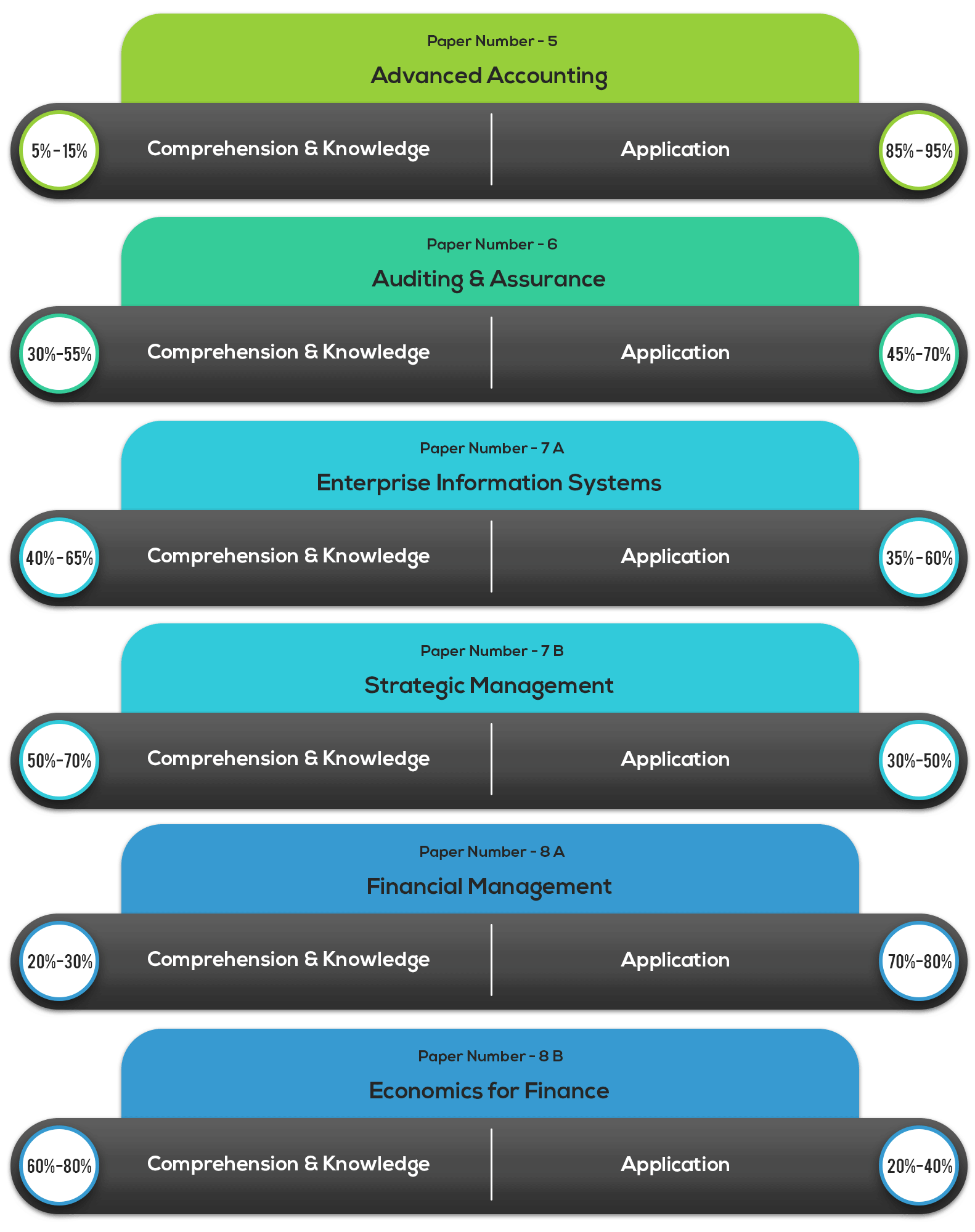
Fig (5): Skill Weightage for CA Intermediate Exam Group II Papers
Now, let’s see what each paper contains.
Group I- Paper 1: Accounting (100 Marks Total; Duration 3 hours)
The first paper of Group I in the CA Intermediate Exam is the Accounting paper. According to ICAI, the objective of this paper is to “acquire the ability to apply specific Accounting Standards and legislations to different transactions and events and in preparation and presentation of financial statements of various business entities.”
Here’s the syllabus:
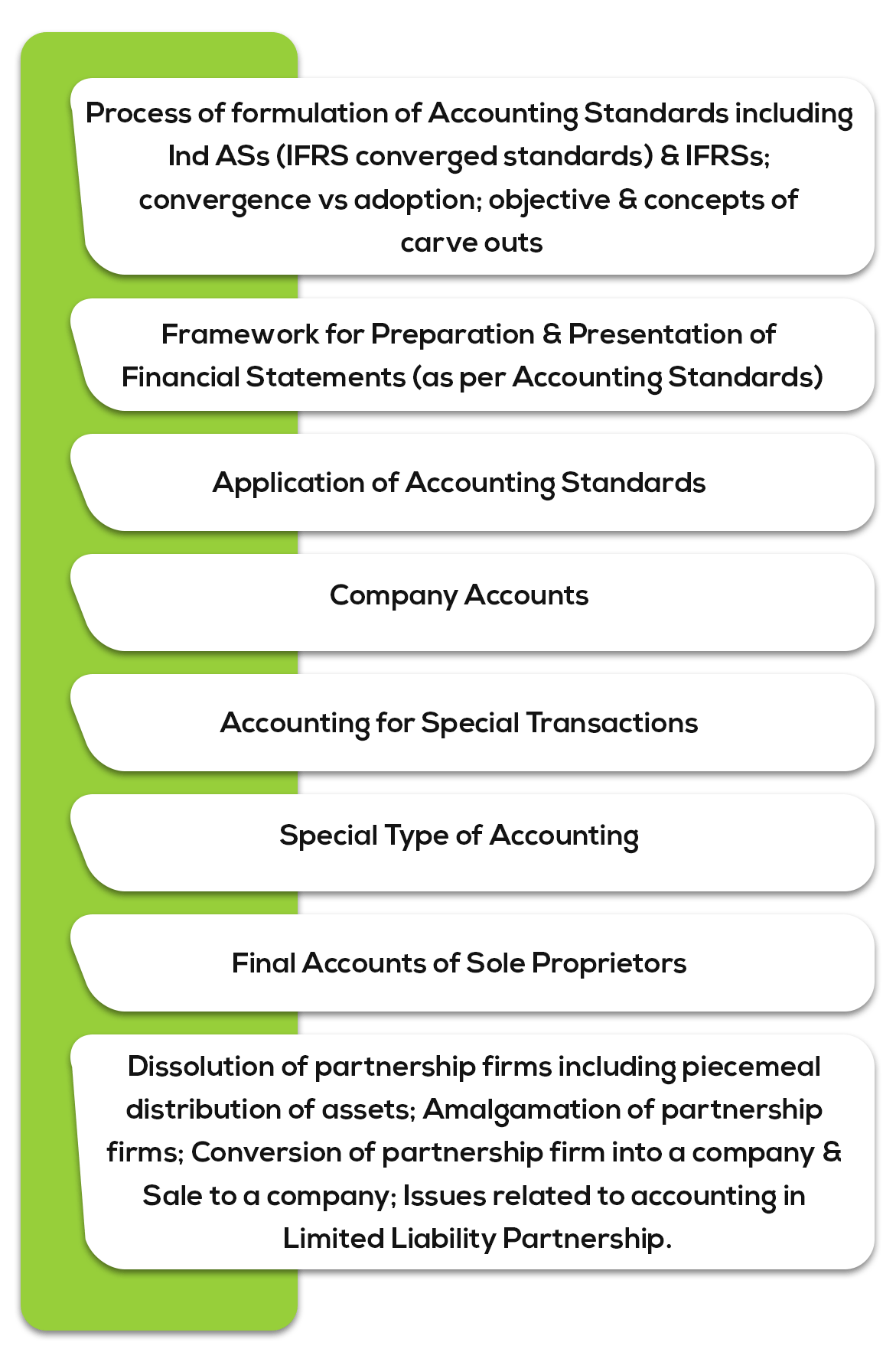
Fig (6): Accounting – Syllabus for CA Intermediate Exam Overview
Note that if new accounting standards, announcements and limited revisions to them are issued, then the syllabus will be updated to reflect them. The same goes for the case where earlier ones are withdrawn or new accounting standards, announcements and limited revisions are issued in place of them. This will take effect from the date to be notified by the Institute.
Group I – Paper 2: Corporate and Other Laws (100 Marks Total; Duration 3 hours)
This paper of the CA Intermediate exam is divided into two parts. Part I and Part II.
Let’s look at what each part contains and the objectives.
Group I – Paper 2 – Part I: Company Law (60 Marks)
The objective is to “develop an understanding of the provisions of Company Law and acquire the capability to address application-oriented issues.”
The contents are as follows:
The Companies Act, 2013 – Sections 1 to 148:

Fig (7): Corporate Laws – Syllabus for CA Intermediate Exam Overview
Note that the provisions of the Companies Act, 1956 that are still in force will form part of the syllabus until such time their corresponding or new provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 are enforced.
Group I – Paper 2 – Part II: Other Laws (40 Marks)
According to the prospectus, there are two objectives:
- To develop and understanding of the provisions of select legislations and acquire the ability to address application-oriented issues
- To develop an understanding of the rules for interpretation of statutes
Here are the topics:

Fig (8): Other Laws – Syllabus for CA Intermediate Exam Overview
Note that if Parliament enacts new legislations in place of existing ones, the syllabus will be updated to include the corresponding provisions of these new legislations. It will be effective from the dates notified by the Institute. Similarly, if any existing legislation ceases to have effect, the syllabus will be updated to reflect the change.
The specific inclusions/exclusions in the various topics covered in the syllabus will be effected every year by way of Study Guidelines, if required.
Group I – Paper 3: Cost and Management Accounting (100 Marks Total; Duration 3 hours)
As per the CA Intermediate syllabus outlined by ICAI, the objectives are:
- to develop an understanding of the basic concepts and applications to establish the cost associated with the production of products and provision of services and apply the same to determine prices; and
- to develop an understanding of cost accounting statements; and
- to acquire the ability to able to apply cost information for cost ascertainment, planning, control and decision making.
The syllabus is divided into four broad subject areas.
These are:
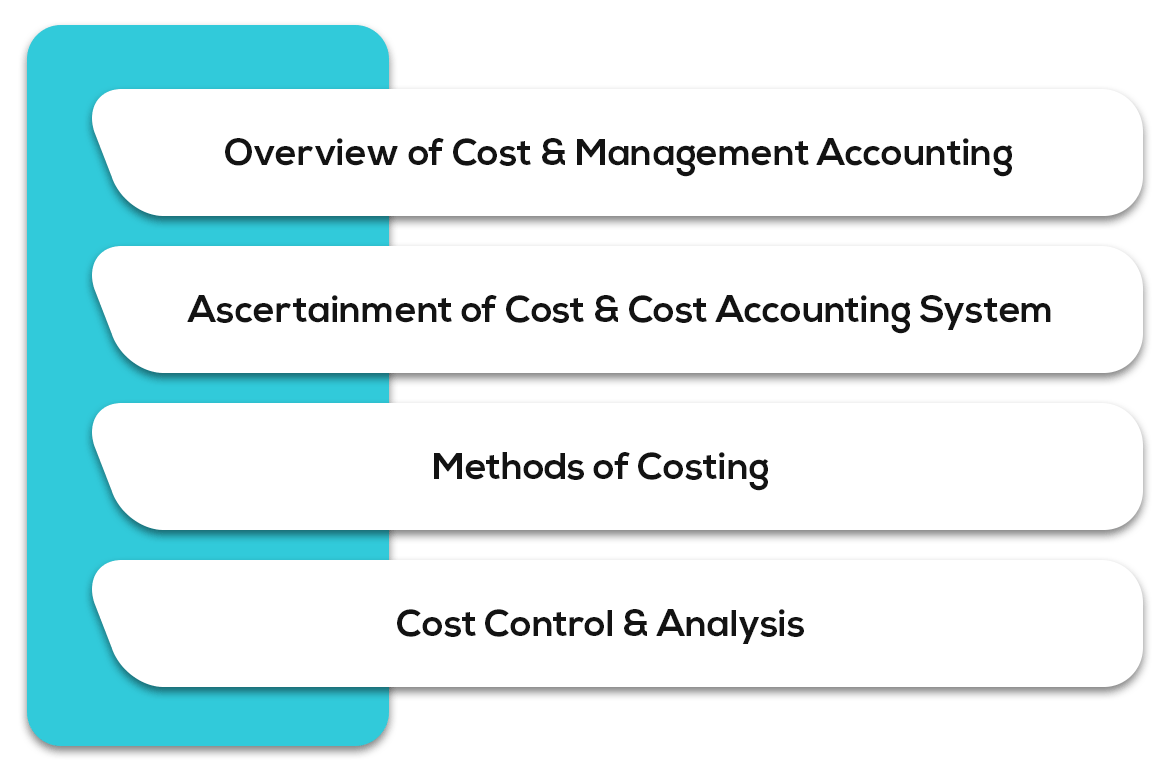
Fig (9): Cost and Management Accounting – Syllabus for CA Intermediate Exam Overview
Under each subject area, there are further subtopics. Let’s see what they are.
Subject Area: Overview of Cost and Management Accounting
Subtopics covered:
- Introduction to Cost and Management Accounting
- Objectives and Scope of Cost and Management Accounting
- The users of Cost and Management accounting information, Functions of management accounting
- Role of cost accounting department in an organisation and its relationship with other departments
- Installation of Costing System
- Relationship of Cost Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting and Financial Management
- Cost terms and Concepts
- Cost Reduction and Cost Control
- Elements of Costs
- Cost behavior pattern, Separating the components of fixed, variable, semi-variable and step costs
- Methods of Costing, Techniques of Costing
- Cost Accounting with use of Information Technology
- Elements of Cost and preparation of Cost Sheets
- Functional classification and ascertainment of cost
- Preparation of Cost Sheets for Manufacturing sector and for Service sector
Subject Area: Ascertainment of Cost and Cost Accounting System
Subtopics covered:
- Material Cost
- Procurement procedures- Store procedures and documentation in respect of receipts and issue of stock, Stock verification
- Valuation of material receipts
- Inventory control
- Techniques of fixing level of stocks- minimum, maximum, re-order point, safety stock, determination of optimum stock level
- Determination of Optimum Order quantity- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
- Techniques of Inventory control- ABC Analysis, Fast, Slow moving and Non moving (FSN), High, Medium, Low (HML), Vital, Essential, Desirable (VED), Just-in-Time (JIT)- Stock taking and perpetual inventory system, use of control ratios
- Inventory Accounting
- Consumption- Identification with products of cost centres, Basis for consumption entries in financial accounting, monitoring consumption
- Employee Cost
- Attendance and Payroll procedures
- Elements of wages- Basic pay, Dearness Allowance, Overtime, Bonus, Holiday and leave wages, Allowances and perquisites
- Employee Cost Control
- Employee Turnover- Methods of calculating employee turnover, causes of employee turnover, effects of employee turnover
- Utilisation of Human Resource, Direct and indirect employee Cost, charging of employee cost, Identifying employee hours with work orders or batches or capital jobs
- Remuneration systems and incentive schemes
- Attendance and Payroll procedures
– Time Rate System, Piece Rate System, Differential piece rate system, Calculation of wages, Effective Wages
- Direct Expenses
- Direct expenses
- Nature of Direct or Chargeable expenses
- Sub-contracting- Control on material movements, Identification with the main product or service
- Overheads
- Functional analysis- Factory, Administration, Selling, Distribution, Research and Development
- Behavioural analysis- Fixed, Variable and Semi- Variable
- Allocation and Apportionment of overheads using Absorption Costing Method
- Factory Overheads- Primary and secondary distribution
- Administration Overheads- Method of allocation to cost centres or products
- Selling& Distribution Overheads- Analysis and absorption of the expenses in products/ customers, impact of marketing strategies, cost effectiveness of various methods of sales promotion
- Treatment of Research and development cost in cost accounting
- Concepts of Activity Based Costing (ABC)
- Recording and Accounting of Costs
- Non-integrated Cost Accounting system- Ledger under non-integral system
- Integrated (Cost and Financial) Accounting system- Ledgers under integral system
- Difference between the Non- integrated and Integrated Accounting system
- Reconciliation of profit as per Cost and Financial Accounts (under Non-Integrated Accounting System)
Subject Area: Methods of Costing
- Single Output/ Unit Costing
- Job Costing: Job cost cards and databases, collecting direct costs of each job, attributing overheads to jobs, Application of job costing
- Batch Costing: Determination of optimum batch quantity, Ascertainment of cost for a batch, Preparation of batch cost sheet, Treatment of spoiled and defective work
- Contract Costing
- Ascertainment of cost of a contract, Progress payment, Retention money, Escalation clause, Cost plus contract, Value of work certified, Cost of Work not certified
- Determination Value of work certified, Cost of work not certified, Notional or Estimated profit from a contact
- Process / Operation Costing
- Process cost recording, Process loss, Abnormal gains and losses, Equivalent units of production, Interprocess profit, Valuation of work in process
- Joint Products- Apportionment of joint costs, Methods of apportioning joint cost over joint products
- By-products- Methods of apportioning joint costs over by-products, treatment of By-product cost
- Costing of Service Sectors
- Determination of Costs and Prices of services of following sectors/ Industries: Transport, Toll roads, Hospitals, Canteen/ Restaurants, Hotels/ Lodges, Educational Institutions, Financial Institutions/ Banks, Insurance, IT sector and other services
Subject Area: Cost Control and Analysis
- Standard Costing
- Setting up of Standards, Types of Standards, Standard Costing as method of performance measurement.
- Calculation and Reconciliation of Cost Variances
- Material Cost Variance, employee Cost Variance, Variable Overheads Variance and Fixed Overhead Variance
- Marginal Costing
- Basic concepts of marginal costing, Contribution margin, Break-even analysis, Break –even and profit volume charts, Contribution to sales ratio, Margin of Safety, Angle of Incidence, Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis (CVP), Multi- product break- even analysis, Consideration of Limiting factor (key factor)
- Determination of Cost of a product/ service under marginal costing method, determination of cost of finished goods, work-in-progress
- Comparison of Marginal costing with absorption costing method- Reconciliation of profit under the both methods
- Short term decision making using the above concepts (basic / fundamental level)
- Budget and Budgetary Control
- Meaning of Budget, Essentials of Budget, Budget Manual, Budget setting process, Preparation of Budget and monitoring procedures
- The use of budget in planning and control
- Flexible budget, Preparation of Functional budget for operating and non- operating functions, Cash budget, Mas